April 13-16, Atlanta, GA
Robotics & Market Insights
Robotic Risk Assessment: Who, Why, and How?
All manufacturers integrating industrial robotics into their facilities should be familiar with the risk assessment process. Risk assessments are crucial in creating a safe and effective workplace environment. The risk assessment is a standardized method of identifying and weighing workplace hazards and determining appropriate action items for risk mediation. This article will cover why risk assessments are important, how to perform one, and what to do with the results.
Who Should Perform a Robotic Risk Assessment (and Why)?
It’s a common misconception that the OEM is responsible for all machine safety concerns, including the risk assessment. In almost all cases, the manufacturer is responsible for performing the risk assessment and mitigation. This makes sense as the manufacturer decides when, where, and how to deploy and operate their equipment. As an example, if a manufacturer purchases a new palletizing robot for their food and beverage operation, it is up to the manufacturer to perform the assessment. Additionally, the responsibility is on the manufacturer to perform risk mitigation on the identified hazards.
Most countries have regulations requiring some form of risk assessment and mediation for manufacturers. For example, OSHA (US), CSA (Canada), and HSE (UK) are all safety regulation bodies with laws on risk assessments. It’s essential to be familiar with the safety codes of your country or region and how they apply to industrial robotics.
Risk assessments are essential because they help identify hazards that can seriously injure machine operators and other employees. Robots can be dangerous for human operators. Mitigation helps manufacturers reduce the likelihood and severity of machine-related injuries. Failure to perform a risk assessment can also lead to severe penalties in many countries.
Risk assessments should be performed in a few basic scenarios:
- When a robot or other industrial machine is introduced to the process
- When processes are modified or machine usage changes
- When new hazards are identified
In cases like these, a risk assessment should be performed to determine risk and appropriate mitigation.
How to Perform a Risk Assessment
It’s clear that risk assessments are a critical component of running a safe operation. This task can appear daunting at first, but risk assessments follow a few simple steps:
- Identify Hazards
- Prioritize Risk
- Mitigation
Thorough documentation will benefit you throughout this process. Prepare to take many photos of the robotic work cell and surrounding area. Perform interviews with staff—including those not directly involved with the robot cell. Knowledge of local regulations will help you understand what actions to take for mitigation.
Determine Goals
Before beginning your risk assessment, it’s helpful to define a few goals for this endeavor. These goals will help you maintain focus and direction during the process. Your goals should include trying to answer the following questions about the safety of your machine operations:
- What could possibly happen, and under what circumstances could it happen?
- How often could this result happen?
- What are the consequences of the potential outcomes?
- How likely are the results to occur?
- Is there additional mitigation that can be done?
These questions can keep you on track to completing a proper risk assessment. In doing so, you can identify what poses the most significant risks to your employees and reduce those hazards.
Identify Hazards

The core component of the risk assessment is identifying hazards. The primary goal is to identify any mechanism, situation, or process where an employee could be injured. During this process, you should talk to as many people involved in the process as possible. For documentation, you should take plenty of photos of the robot in and out of operation. Additionally, it’s often helpful to have people both experienced with and new to the machine and process to review potential hazards. This helps give a complete picture of possible risks through both experienced and fresh perspectives.
How to Identify Hazards
When you’re in the process of identifying hazards, it helps to make a few considerations:
- Which components propose apparent risks?
- Examples: Robot arm, flying shear, flywheel, pinch points, etc.
- Consider the entire process from start to finish
- Review different ways that operators interact with the robot/machine
- Consider ways in which operators could improperly interact with the robot/machine
- Look at how employees not directly involved with operating the robot could come into contact with hazards
- Logistics operators, cleaning crews, etc.
- Review previous incident reports
- Examine maintenance procedures for potential risks
- Review work cell access to employees outside of regular operators
- Admin staff, visitors, etc.
Here’s an example of what an identified hazard might look like:
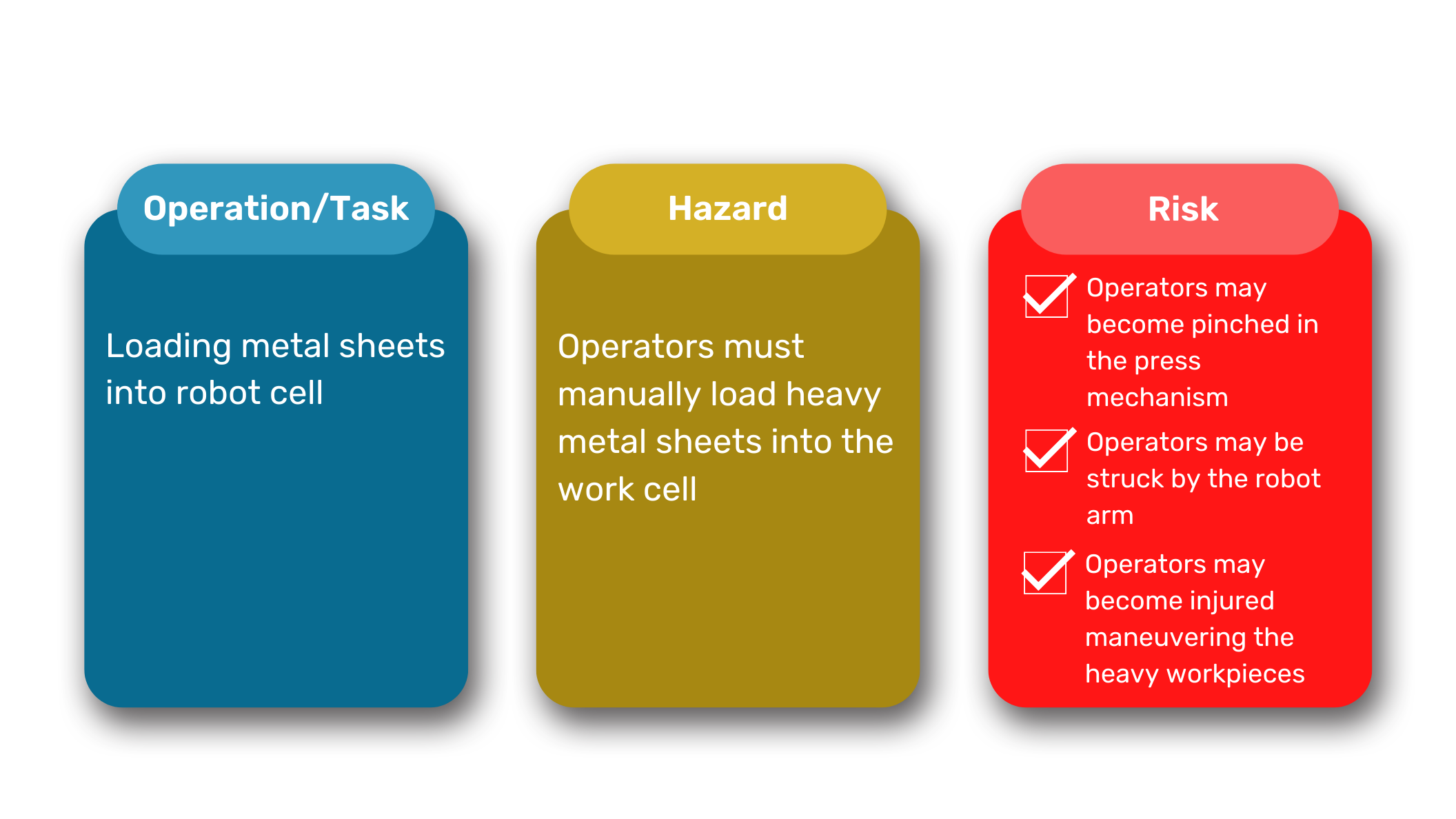
You should compile a long list of operations or tasks, potential hazards, and their associated risks. This way, you more clearly understand the possible dangers facing your employees.
How to Determine Risk
Determining risk can sometimes be a tricky process. Sometimes it’s unclear whether a process or mechanism poses a risk.
Here are some things to consider to assess risk:
- Consultation from a certified safety representative
- Opinions of experienced operators
- Safety Data Sheets and machine manuals
- Local regulations and best practices
- Length and intensity of exposure
- Related incidents from comparable machines
- Test results
Prioritize Risk
Prioritizing risk is another critical component of the risk assessment process. You can evaluate priority by analyzing the severity of the risk and the likelihood of the incident occurring. Ranking the risks allows you to determine which hazards to address first.
Creating a ranking can be an inexact science. The final order often comes down to judgments made by a team of people with individual perspectives, biases, interpretations, and knowledge of the workplace procedures. However, as long as everyone maintains the same goals, a reasonable conclusion of risk should be reached.
Reaching a Conclusion
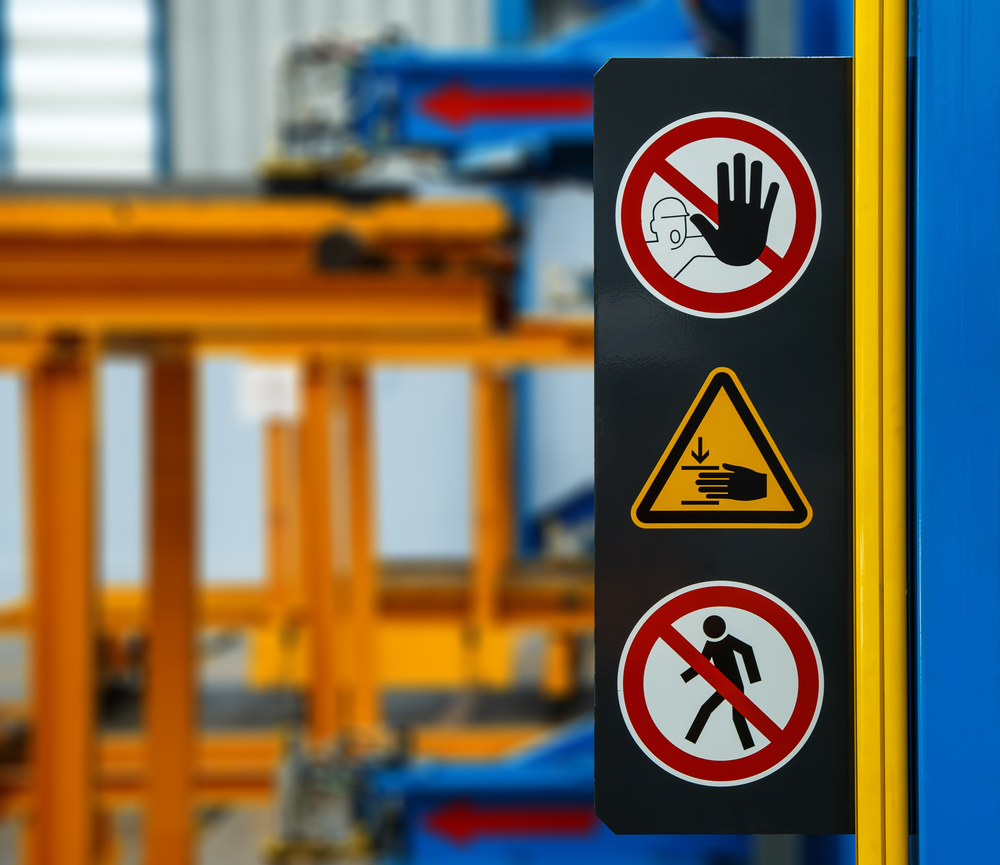

Once you’ve identified and ranked your facility's risks, you can move forward with mitigation measures. This is the process of reducing the risks posed by the previously identified hazards. You should reference existing rules and regulations when determining mitigation steps. There are a few different common methods of mitigation:
- Total elimination
- Removing the hazard completely, blocking the hazard from access, removing the process, etc.
- Electrical or automated controls
- Installing light curtains, emergency stops, safety scanners, safer programming practices, etc.
- Improving workflows
- Introducing safer working procedures, standards, PPE, etc.
No matter what you decide to do to reduce the risk, you should aim to reduce the severity and probability that an incident will occur. This will maximize the benefits you gain from your robot investments by improving your facility's safety. This increase in workplace safety will create a happier, safer, and more efficient working environment.
